Applications
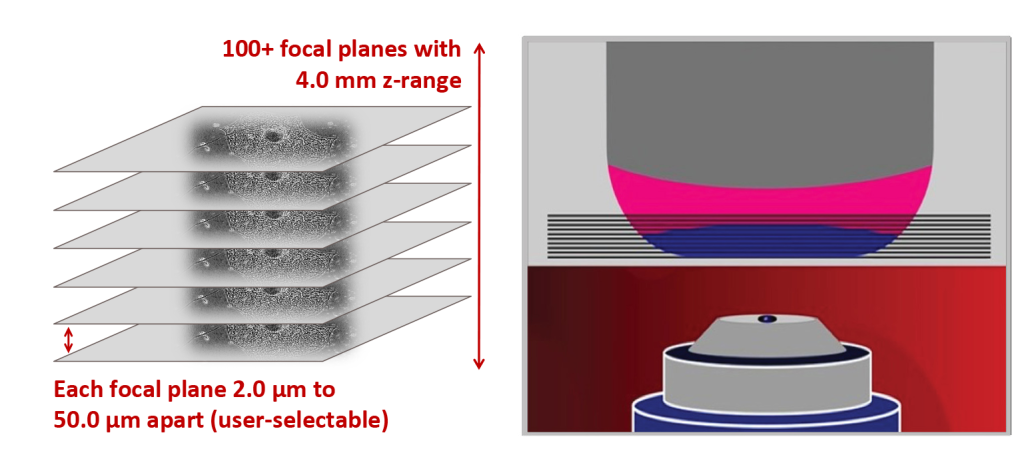
Image Tissues, Suspension Cells, and Adherent Cells with 100+ Focal Planes
- The CellAssist captures bright-field and phase contrast images at 100+ focal planes, 2 µm to 50 µm apart.
- Users can select the number of focal planes and distance between them depending on the experiment.
- Each image is five megapixels and 500 to 20,000 images are captured rapidly, stitched together, and added to a centralized database.
- Gain deeper insights into cell morphology with the CellAssist!
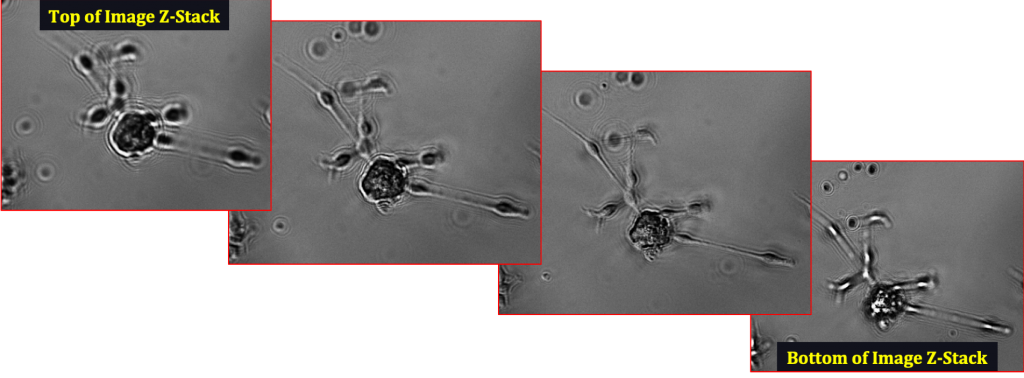
Neurosphere differentiating into a neuron, imaged on the CellAssist in a 96-well round-bottom plate at 10x resolution in bright-field
Quantitatively Assess Cell Growth and Confluence
CellAssist measures cell growth through doubling time measurement:
- CellAssist provides several options for measuring cell growth:
- Doubling time
- Doubling rate per hour
- Doubling rate per day
- Allows for precise determination of growth rates through manually defined start and end points.
- Enables users to assess confluence more accurately within the selected data set to better predict passage times.
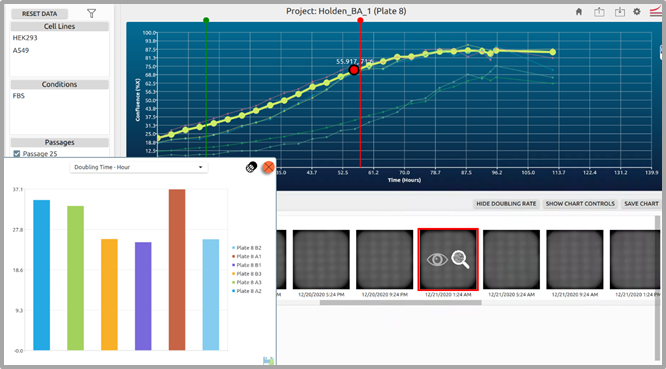
HEK293, and A549 in each well of a 6-well plate. Images were collected every 4 hours for a period of 5 days. During the course of this experiment, 27 standard scans (4x bright-field) were collected, and automatically analyzed for confluence by the CellAssist software.
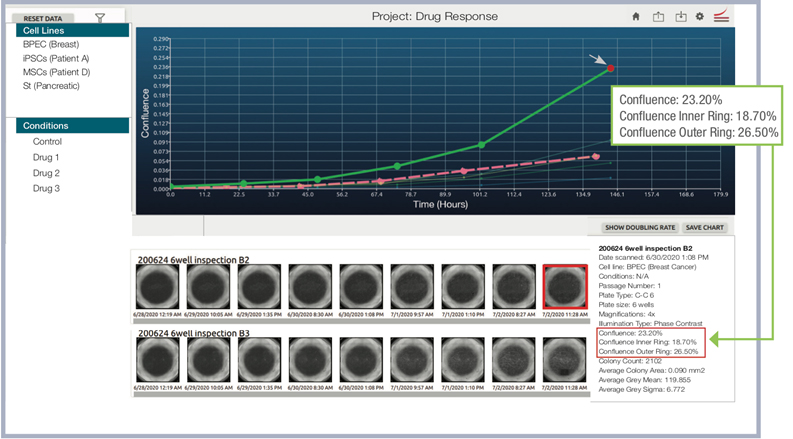
Confluence Measurement in Center and Outer Rings of the Well
Objective metrics, and images for consistent decision-making
CellAssist accurately measures confluence both in the center, and outer rings of the well, which are typically more challenging to analyze.
- Compare and optimize processes
- Identify outliers that are evidence of process problems
- Forecast optimal passaging times
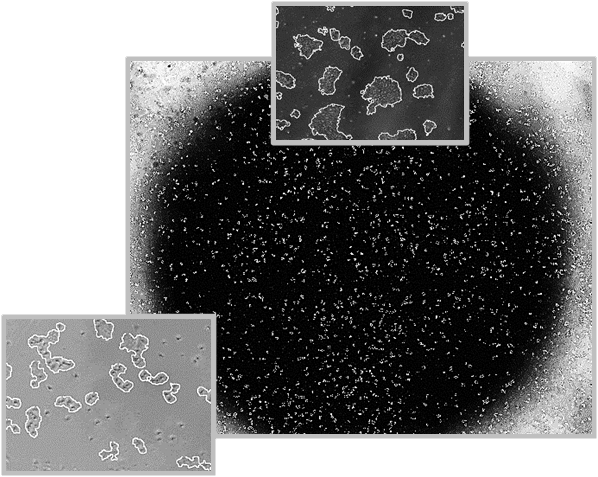
Whole Cell Imaging and Segmentation
The CellAssist offers the option to acquire quick scan images (selected areas of the well), or expertly stitched whole-well images
- Users are able to view images by spatial coordinates throughout time, enabling robust time-lapse imaging for any region of interest, including the whole well.
- A stitched whole-well image of a 6-well plate is shown on the right with colony outlines identified by Thrive Bioscience algorithms
Deeper Insight into Cell Morphology with Time-Series Images
Daily scans show the capability of CellAssist to follow colonies or a region of interest over time.
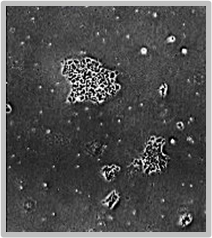
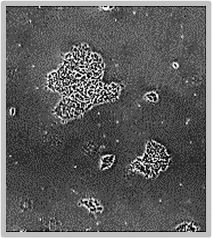
Day 2
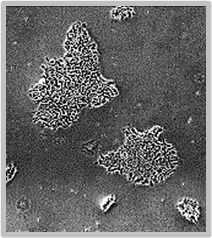
Day 3
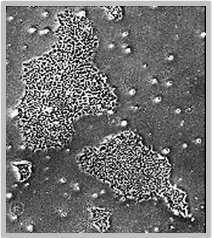
Day 4
Colonies imaged in 6-well plates at 4x resolution
Analysis of Outliers to Improve Quality
CellAssist improves quality, and documentation of cells
Problem:
Current tools do not collect images and data along with tools that enable users to visualize outliers. Outliers are important because they may indicate problems in quality that require investigation.
Objective:
Document and analyze images and data on cells over time to improve quality and reproducibility of cell, tissue, and suspension cultures.
CellAssist Solution:
CellAssist provides comparable data over time that allows for identification of outliers.
(In this example, upon further investigation, the customer found cases of mislabeling.)
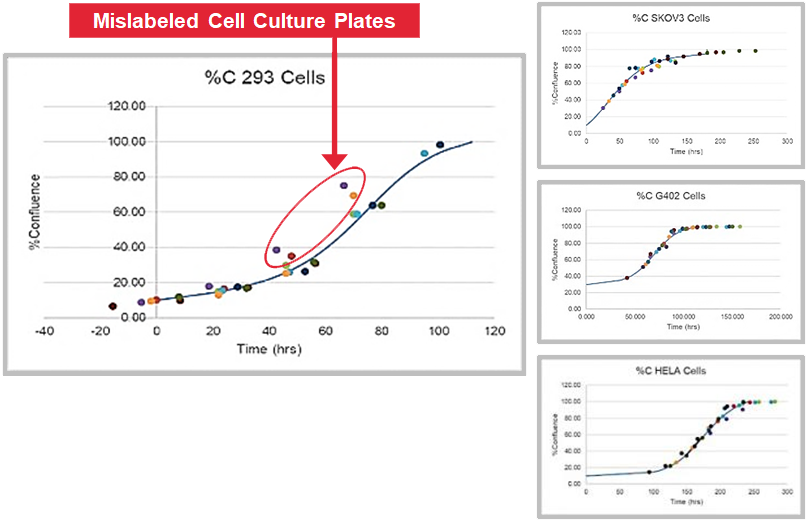
(Statistical anomaly highlighted)
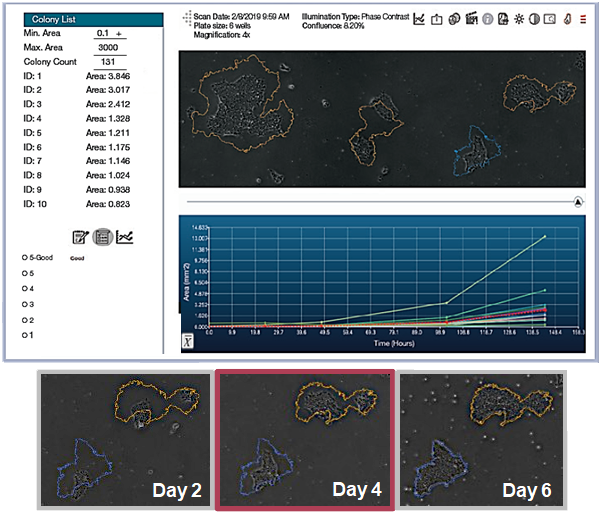
Monoclonality Probability of Candidate Colonies
CellAssist improves quality and increases yield by using data to grade and pick colonies
Problem:
Gene editing transfection rates can be poor, so it is crucial to select monoclonal colonies for passaging.
Objective:
Accurately determine whether a colony is monoclonal by capturing a series of time lapse images with excellent registration across scans.
CellAssist Solution:
The CellAssist time-lapse imaging enables the lineage of candidate colonies to be tracked to a single starting cell.
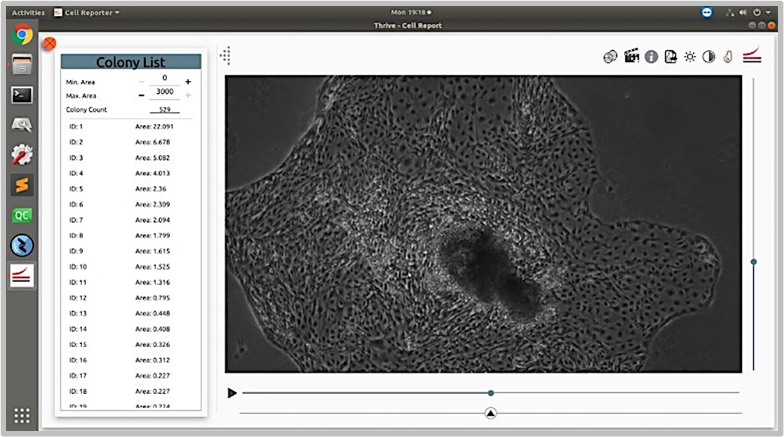
Morphological Assays for iPSC to Glial Cell Transformations
Morphological assays do not disturb cell growth
Problem:
Differentiation of neuronal progenitor cells into glial cells was measured using fluorescence-based end point assays, which did not allow for further growth and study of the cells. An equivalent assay was needed based on imaging of live cells.
Objective:
Acquire high-resolution images that are comparable over time in order to study differentiation without dyes and/or probes that interfere with the cells and colonies.
CellAssist Solution:
The CellAssist’s high-resolution stacks of images, with highly accurate registration across scans, enabled the characterization of cell morphology without disturbing the cells and colonies.
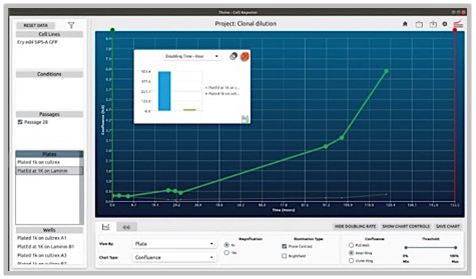
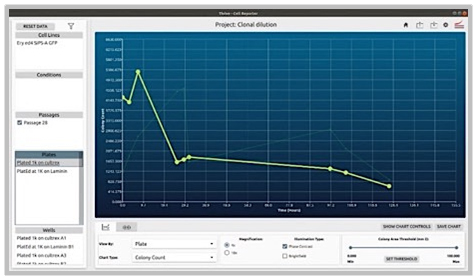
Comparison of Cell Growth on Various Plate Surface Coatings
Problem:
1.) The coating of plates can profoundly affect the survivability and growth of colonies (in this case gene edited ones starting with very small quantities).
2.) Some coatings are also significantly more expensive.
Objective:
1.) Coating Comparison: Evaluate and compare two different coatings by observing and characterizing the behavior of cells under each condition over a set period. This analysis will help determine which coating optimally supports cell health and activity.
2.) Protocol Optimization: Develop, implement, and assess new protocols tailored to these coatings. By directly comparing the results, identify the most effective protocol and coating combination that enhances experimental outcomes.
CellAssist Solution:
The CellAssist’s documentation, colony counting curves, and examination of images are used to characterize the number of colonies for each condition, and the results are collated and easily compared across conditions.